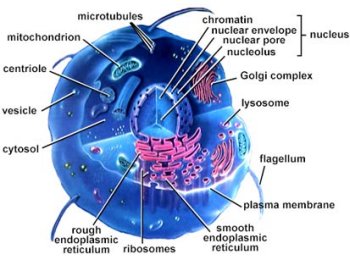
|  | Definitions: (Ignore all the A's at the ends of these words) Centrioleí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A cylinder-shaped organelle composed of microtubules and found in the nucleus of a cell. During nuclear division it forms the spindle, which ensures that the duplicated chromosomes are equally divided between the daughter cells. Resembles a basal body in structure. Centrioles are not found in plant cells.
Chromatiní¹‚í°¦lt;br>The tangled fibrous complex of DNA and protein within a eukaryotic nucleus.
Cytosolí¹‚í°¦lt;br>The fluid portion of a cell's cytoplasm.
Flagellumí¹‚í°¦lt;br>a long structure that aids eukaryotic cells in movement
Golgi Apparatusí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A cellular organelle of the cytoplasmic membrane. It is covered with cisternae and is involved in secretory processes.
Lysosomeí¹‚í°¦lt;br>a small sac inside the cell cytoplasm that digests food, cell debris, bacteria. And other foreign subtances
Microtubulesí¹‚í°¦lt;br>Thin tubes made up of protein that are used to make structures involved in cellular movement such as flagella.
Mitochondrioní¹‚í°¦lt;br>an organelle of eukaryotic cells; the site of ATP production and cellular respiration
Nucleolusí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A dense, roughly spherical body found within the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
Nucleusí¹‚í°¦lt;br>a large cellular organelle that contains DNA; the region of an atom containing protons and neutrons
Plasma Membraneí¹‚í°¦lt;br>The membrane that surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, separating it from the environment. It consists of a double layer of phospholipids and has proteins embedded in it.
Ribosomeí¹‚í°¦lt;br>an organelle located in the cytoplasm of cell; site of RNA translation
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulumí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A type of endoplasmic reticulum, an organelle found in eukaryotic cells, which has a large number of ribosomes attached all over it. It is important to the making of proteins and in preparing secretions of the cell.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulumí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A type of endoplasmic reticulum, an organelle found in eukaryotic cells, which plays an important role in the making of steroid hormones.
Vesicleí¹‚í°¦lt;br>A bubble within the cell which is surrounded by
cell membrane material and is formed by pinching off part of the cell membrane. Vesicles contain particles which the cell is importing ( endocytosis), or waste products and secretions which the cell is exporting (exocytosis).
|





